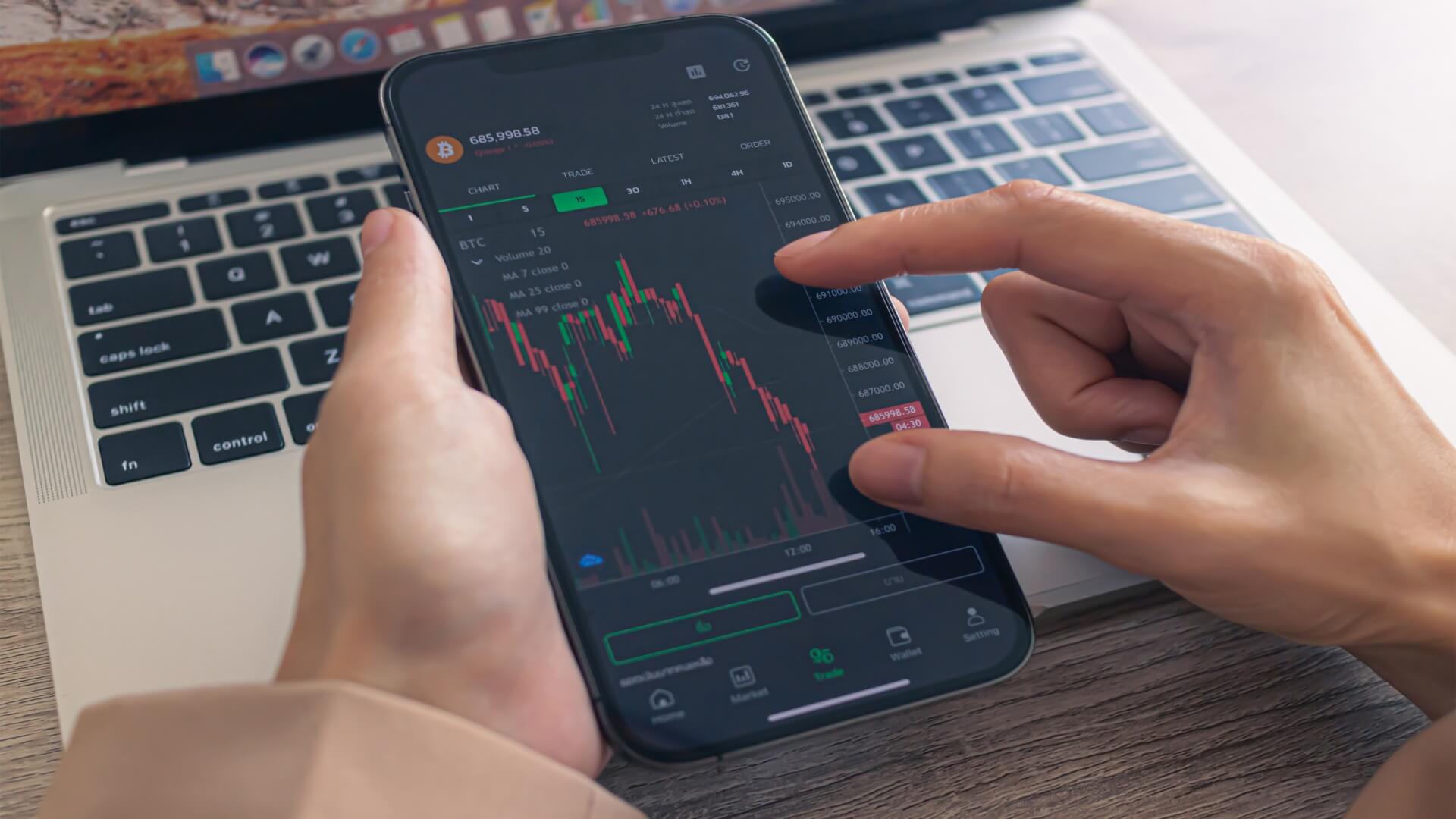
Cash index trading refers to the buying and selling of financial instruments based on the value of a specific stock market index. This type of trading has become increasingly popular among investors because it allows them to gain exposure to an entire market or sector without having to purchase individual stocks.
Cash index trading provides investors with a way to diversify their portfolios and manage risk more effectively. It also provides opportunities for traders to profit from short-term price movements in the markets. However, regulations governing cash index trading are necessary to ensure fair and transparent practices and protect investors from fraud or manipulation.
Overview of Regulations
In many countries, cash index trading is regulated by financial regulatory authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia. Traders must understand the regulations for trading Cash Indices efficiently.
These regulatory bodies enforce rules and regulations that govern various aspects of cash index trading, including disclosure requirements for market participants, minimum capital requirements for traders and brokers, restrictions on insider trading, and measures to prevent market manipulation.
One example of the importance of regulations governing cash index trading can be seen in the case of the 2010 “Flash Crash” in the United States. On May 6, 2010, the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped nearly 1000 points within minutes before quickly recovering. This sudden and severe drop was caused by a combination of high-frequency trading algorithms and human error, which led to a cascade effect across multiple markets.
In response to this event, regulators introduced new rules aimed at preventing future market disruptions. These rules included circuit breakers that automatically halt trading when stock prices move too quickly in either direction and increased monitoring of high-frequency trading activity. These regulations have helped to restore confidence in the markets and prevent similar events from occurring again.
Overall, regulations governing cash index trading play a crucial role in ensuring fair and transparent practices within financial markets. While some may argue that excessive regulation can stifle innovation or limit market participation, it is important to strike a balance between promoting growth and protecting investors from fraudulent activities or market disruptions that can have far-reaching consequences for individuals and society as a whole.
Compliance Requirements
Market participants in cash index trading are required to comply with various regulatory requirements to ensure fair and transparent practices. One such requirement is the disclosure of all relevant information to investors, including risks associated with the investment and fees charged by brokers.
Additionally, traders and brokers must maintain minimum capital requirements to ensure they have sufficient funds to cover potential losses. Market participants must also adhere to rules prohibiting insider trading, which involves using non-public information for personal gain or sharing it with others who may use it for their benefit. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal action, or revocation of licenses required for operating within the financial markets.
As an example, here are some consequences of failing to comply with regulations in cash index trading can be seen in the case of Rajat Gupta, a former board member at Goldman Sachs. In 2012, Gupta was convicted of insider trading after he leaked confidential information about the bank’s earnings and investments to hedge fund manager Raj Rajaratnam. The information allowed Rajaratnam and his firm to make millions of dollars in profits from trades based on insider knowledge.
Market participants must ensure that they do not use non-public information for personal gain or share it with others who may use it for their benefit. Failure to comply with these regulations not only puts investors at risk but can also result in severe legal consequences for those involved. Compliance requirements for market participants play a crucial role in promoting fair and transparent practices within financial markets.
Conclusion
Cash index trading is an important tool for investors to diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively. However, regulations governing cash index trading are necessary to ensure fair and transparent practices in the markets.
By promoting transparency, and protecting investors from fraudulent activities or market disruptions, these regulations help support a healthy economy for all.